Do you know the EB electron beam coating curing technology? Can it bring about a new revolution in panel finishes?
2023-04-11 17:16
Do you know the EB electron beam coating curing technology?
Can it bring about a new revolution in panel finishes?
At present, many brands use the "Electron Beam Curing" when describing the panel finishing process, which is directly translated as "Electron Beam Curing" and belongs to a new type of coating drying or curing technology.
For the drying technology of surface coatings on furniture products, we are familiar with hot air drying (thermal curing), infrared drying, UV drying (ultraviolet drying), microwave drying, etc. However, "electron beam curing technology" seems to be completely unknown in terms of both technical concepts and principles, which undoubtedly aroused our great interest.
Therefore, we hope to introduce EB curing technology through this article, so that everyone can understand what electron beam curing is? What are the differences and characteristics compared to other coating curing technologies? How can it be applied in furniture panels and what are its future prospects?
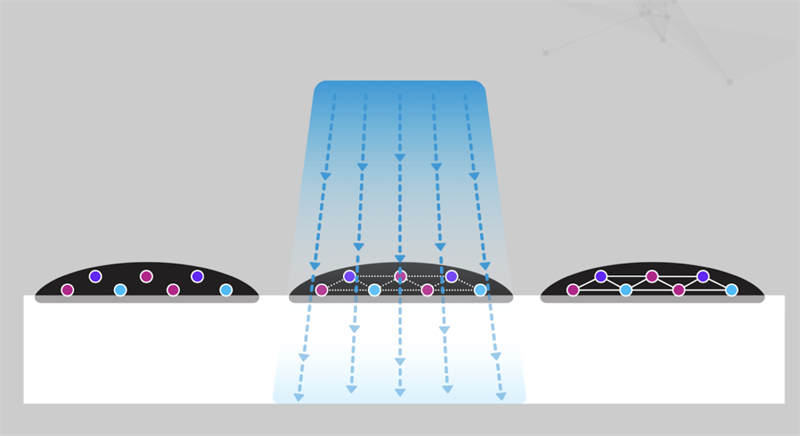
01 What is EB electron beam curing technology?
The most direct way to understand a new technology is to start with its name and concept. The full English name for this technology is "Electron Beam Cured", also known as "Electron Beam Curing (EBC)", which refers to the technology of using electron beams for coating curing. So the question also arises, what is "electron beam (EB)"? Why can it achieve the effect of curing the coating?
01-1 EB Electron Beam Curing Principle
At the microscopic level, all atoms are composed of a positively charged atomic nucleus and a number of electrons moving around it. Electrons are the first elementary particle found and are negatively charged.
The electrons generated by the cathode in the electron gun are accelerated to a very high speed under the action of a high-voltage accelerating electric field between the cathode and anode. After convergence, they form a dense high-speed electron flow, known as an electron beam (EB).
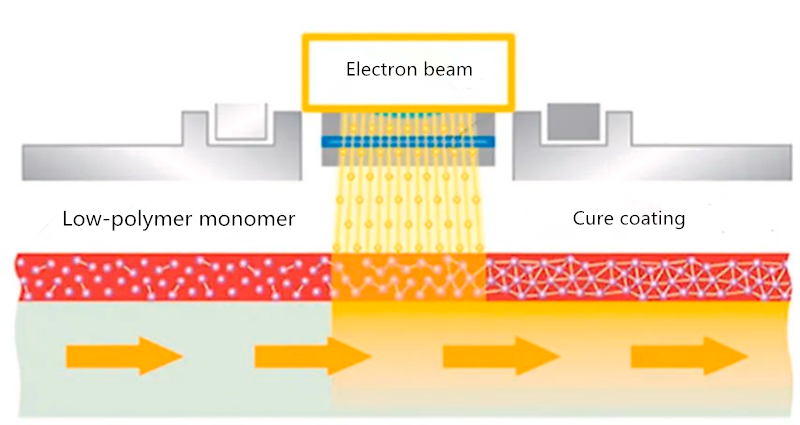
When a high-energy electron beam acts on a coating, it can cause unsaturated molecules to form active free radicals in a few seconds or even less, triggering the polymerization of unsaturated resins and monomers, forming a three-dimensional cross-linking network, thereby inducing the rapid transformation of liquid oligomers into solids through cross-linking polymerization.
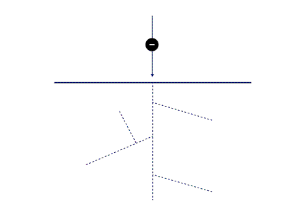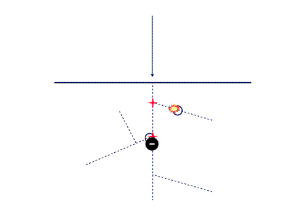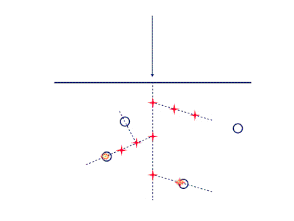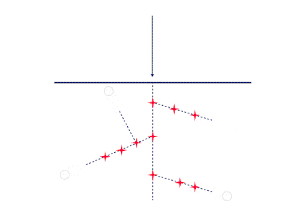
This dynamic effect demonstration diagram well explains the process of EB curing, where the coating molecules undergo changes under the "bombardment impact" of the electron beam. These changes, also known as "cross-linking polymerization," enable the liquid to become a solid.
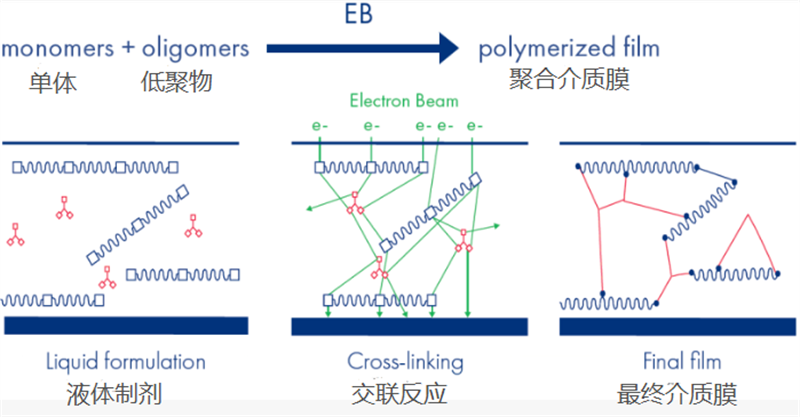
01-2 EB Development and Origin of Electron Beam Solidification.
The earliest application of EB curing technology abroad was by Ford Company in the United States. In the 1970s, Ford applied EB curing technology to the coating of automotive components.
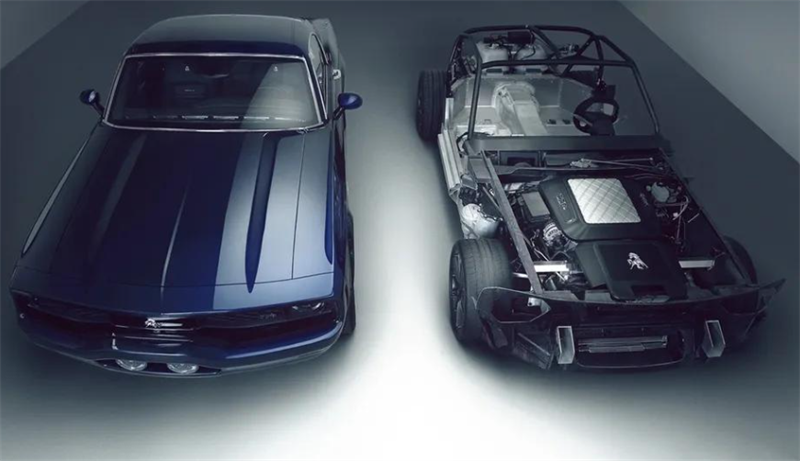

In fact, EB curing can be widely used in the fields of printing and coating, such as milk boxes for breakfast, cars for going out, beverage cans for buying at will, books or magazines for reading on the road, airplanes for looking up, and so on. They may all be applications of electron beam curing.

The situation in China was around 2004 when some printing companies began to introduce EB curing equipment, but it was mainly used for the coating of gloss oil; The attempt to use EB curing for home panels has only been explored by a few domestic enterprises in recent years.

Since EB electron beam curing is also a coating curing method, what is the difference between it and the well-known thermal curing and UV curing? How does EB curing perform in terms of core indicators such as curing energy consumption and curing time, environmental characteristics, and coating quality?
We have searched a lot of information and found a comparative table of three coating curing methods, which well displays the differences between different curing methods. Now, it is organized as follows:
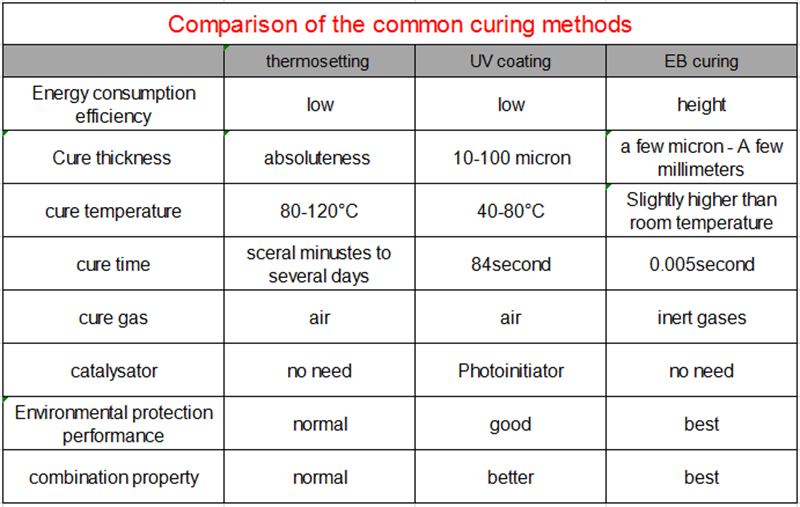
02-1 Curing Energy Consumption and Curing Time.
Under the same curing amount, if the energy consumption of thermal curing is 100%, relevant data shows that the energy consumption of EB curing accounts for 5% of UV curing and 1% of thermal curing, which means that EB curing has the highest energy consumption efficiency under the same conditions.
In terms of curing time, thermal curing takes the longest time, ranging from a few minutes to several days to achieve complete drying of the coating; The UV curing time will be much shorter, only a few seconds; The curing time of EB reached an astonishing 0.005 seconds, which can be said to complete the coating curing in an instant.

02-2 Environmental Protection Characteristics and Coating Quality
For heat cured and UV cured coatings, solvent processes are often used. If organic solvents are used, there will be environmental issues during the production process. Of course, water-based coatings using water as the solvent will not have such problems.
EB curing is a solvent-free process, with a coating solid content of up to 100%. Volatile organic compounds such as VOC have been eliminated from the raw material, making it highly environmentally friendly.
In terms of coating quality, there are several core indicators, such as coating adhesion, coating hardness, tensile strength, yellowing resistance, etc. Experimental data shows that the coating cured with EB has the best comprehensive performance. Especially in terms of yellowing resistance, EB cured coatings have better yellowing resistance as they do not require substances such as photoinitiators.
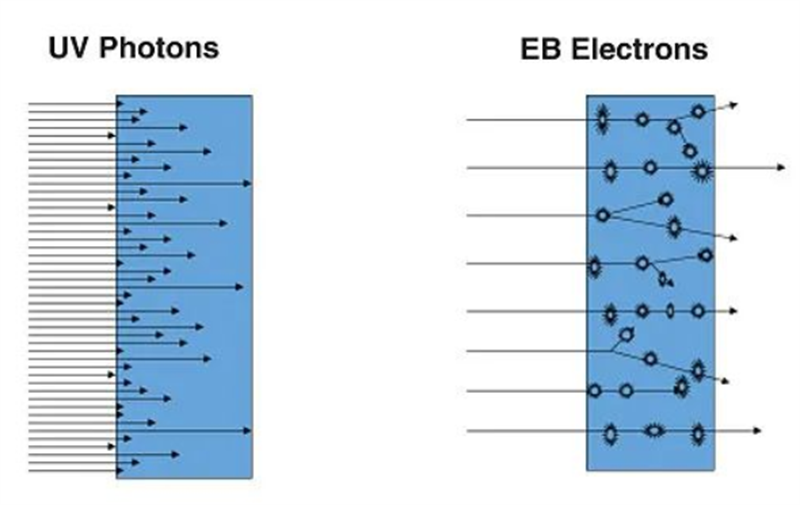
Overall, radiation curing technology mainly includes two types: UV curing and EB curing, both of which use energy irradiation to react and quickly solidify liquid materials. Due to its lower environmental pollution compared to traditional thermal solidification, radiation solidification has rapidly increased its popularity in the context of energy conservation, emission reduction, and sustainable development.
Among them, UV curing uses UV as the irradiation energy, which has the advantages of relatively stable reaction and small equipment investment scale. It is widely used and is currently the mainstream radiation curing technology.
UV curing has the disadvantages of poor penetrability and incomplete curing, and its curing material requires the addition of photoinitiators, which can easily lead to incomplete reaction and residue; Compared to EB curing, it can achieve deep curing, faster curing speed, and complete curing. Moreover, there is no need to add photoinitiators in the curing material, which has high safety and a wider range of applications.
03 Application of EB Curing in Home Panel
The application of EB curing technology in home panels is often found in imported decorative panels. For example, some Italian and Korean board brands emphasize the use of EB curing in their process descriptions. The main board properties include "soft touch, extremely matte, fingerprint proof, and repairable", which is a typical high-end board positioning.

The "hot repair" function among them is quite interesting to the author. In the impression of most of us, if the surface of the board is scratched, the result is irreversible, which means it cannot be restored to its original state. However, EB cured coatings have stronger thermal repair properties due to their strong tensile strength, high fracture elongation, good softness and elasticity. Although it should only be used to repair minor scratches, it is also an innovation and breakthrough.

The high cost should be the primary reason. From the perspective of equipment, EB curing requires the development of professional curing equipment, which is expensive and requires high maintenance costs; From a construction perspective, the EB solidification process needs to be carried out in an inert gas environment, which increases the cost of use; From the perspective of consumables, EB curing materials use EB coatings. Although there is no need to add photoinitiators, the purity requirements for other constituent materials are high, and other high value-added materials will also be added, resulting in high product prices. Overall, the cost of EB solidification is high and the market size is small globally.

We need to recognize that the market awareness of EB curing still needs to be continuously improved. In the future, with the continuous decrease of costs, EB curing is expected to gradually gain market recognition due to its excellent performance, and EB curing decorative panels can also be more popularized and applied.
PS: Zhihua Group has been specializing in home decoration materials for 25 years, mainly producing products such as EB SINAI decorative film/film, PETG film/sheet, acrylic sheet, UV board, PET board, EB board, acrylic MDF board , and matching color edge banding .
Welcome inquiry: 0086-18676549165, email: dayipetg@163.com.








